Promoting Sustainable and Integrated Noncommunicable Disease Surveillance
16.02.2018
Global
TQS
Tobacco use is a leading cause of preventable death in the world and a risk factor for four major noncommunicable diseases (NCDs): cancer; cardiovascular disease; diabetes; and chronic respiratory diseases. About 6 million people die annually from tobacco, and if nothing is done to reverse or halt the epidemic, tobacco-related deaths could rise to 8 million by 2030. Additionally, exposure to secondhand smoke kills more than 600,000 nonsmokers each year.
While the burden of tobacco use is high, there are effective and proven-to-work tobacco control solutions. Country-level interventions that align with the World Health Organization Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) articles—especially the demand reduction measures under mPOWER—have demonstrated declines in tobacco use, resulting in lives saved. Accelerating these evidence-based interventions will only further reductions in tobacco use, which can have implications on other areas of public health including NCDs, reproductive health and communicable diseases.
Efficiencies of Integrating Tobacco Questions for Surveys (TQS)
Launched in partnership with WHO and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), TQS is a list of 22 survey questions, grouped according to mPOWER classifications, that ensure consistent reporting with the Global Adult Tobacco Survey (GATS). TQS offers flexibility through seamless integration into national and international surveys—increasing the pool of reliable results and quality estimates. TQS is also a surveillance tool that can help integrate data on tobacco use with data on NCDs and risk factors. Additionally, survey integration allows for shared financial and human resources, increasing efficiency.
TQS is a part of the Global Tobacco Surveillance System (GTSS)—a set of surveillance tools that are internationally recognized for their standardization, rigor and accuracy in systematically monitoring tobacco use among youth and adults. WHO, CDC and the Canadian Public Health Association (CPHA) launched GTSS in 1999 to help countries generate reliable, accurate and comparable data on the burden of tobacco use and measure progress of tobacco control efforts over time. This system generates nationally representative data on tobacco use at a global level, which can help guide policies and programs.
Continuous monitoring of tobacco use can support countries with tracking targets and indicators under the WHO Global Monitoring Framework (GMF)—which has a specific target of reducing tobacco use by 30 percent by 2025 (using 2010 as a baseline).
Support of Global Partners
The TQS Global Alliance promotes integrating TQS into surveys around the globe. The Alliance includes representatives from various international surveillance systems, research organizations (e.g. academia, public health institutes) and countries (e.g. national statistical agencies, ministries of health) who recognize the value of strengthening systematic tobacco use monitoring and key tobacco control measures.
In 2013, representatives set a target to apply TQS in 70 countries by 2016. Since then, WHO has integrated TQS into their STEPwise approach to Surveillance (STEPS) core questionnaire—which is a simple, standardized method for collecting, analyzing and disseminating data in WHO member countries. The Demographic and Health Survey (DHS) also recently included a few TQS questions into their core “Man’s Questionnaire.”
TQS is a cost-effective and sustainable option for monitoring the tobacco epidemic. Over 79 countries have integrated TQS between 2009 and 2017.
TQS features include:
- A sustainable and cost-effective way to continuously collect data on tobacco use.
- Consistency in reporting results across countries.
- Flexibility through seamless integration into national and international surveys.
- An increased pool of reliable, high-quality data on tobacco use.
- Availability in Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Portuguese, Russian and Spanish.
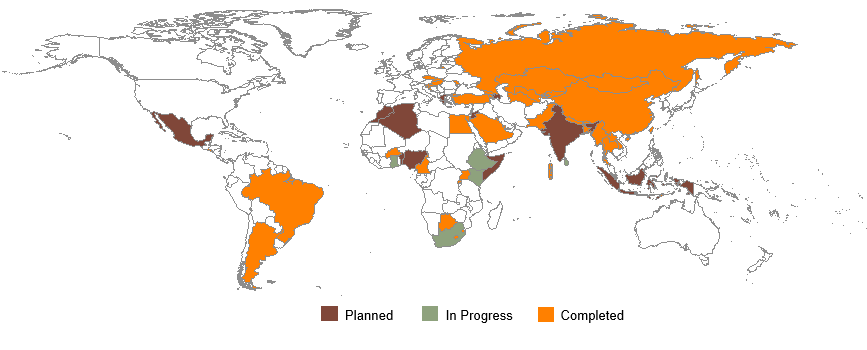
TQS implementation 2008-2017